Objectives
Competing with PVs imported from outside of Europe in terms of prices is still challenging. Expanding the production capacity is one way to face this challenge, however, a more effective way is to introduce innovations.
This is precisely what SHINE PV will do: develop manufacturing lines which will reduce the use of silver and cutting edge induced losses, produce modules of superior electrical properties and reliability, and increase cell efficiency by 0.5% compared to the current technologies on the market.
Based on our knowledge, no other company is currently developing similar technologies which will give SHINE PV a market advantage. Introducing new disruptive PV technologies will improve Europe’s market positioning and certainly help it regain technological leadership in this domain. Strengthening Europe’s scientific and innovation base is the key element for market differentiation and rebalancing global PV market.
Technological innovation
SHINE PV project will focus on the two final steps: cell and module production.
The back-end cell processing will be investigated for the two most promising solar cell designs: Silicon HeteroJunction (SHJ) and Tunnel Oxide Passivated Contact (TOPCon), involving the three key steps in the back-end manufacturing: metallization, post-processing and interconnection.
- For the metallization step, SHINE PV will introduce parallel dispensing and plating as HVM alternative processes to incumbent screen printing, with the objective of demonstrating the complete or partial replacement of Ag with Cu, a fundamental step to enable Tera-Watt scale production levels.
- Moreover, SHINE PV will increase the efficiency (of SHJ) through cell post-processing by applying Light Soaking (LS) process in HVM and recover the cutting-induced losses by Edge Re-Passivation (ERP) of the cells (SHJ and TOPCon) before the module assembly, with a significant benefit in terms of levelized cost of electricity (LCOE).
- For the module making step, the innovations in interconnection proposed by SHINE PV are Twill and Shingling processes and HVM equipment. Both will leverage on the optimization of the metallization and post-processing steps and will demonstrate their potential in terms of superior electrical properties, aesthetics, reliability, and compatibility with premium module designs (for example building integrated PV (BIPV)).
- SHINE PV will identify synergies and differences between SHJ and TOPCon and will demonstrate different flows and down select the most promising ones in terms of cost of ownership (CoO) and high-volume manufacturing (HVM) readiness.
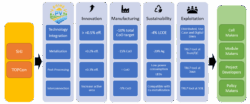 Key elements and metrics of SHINE PV project throughout the different technologies developed
Key elements and metrics of SHINE PV project throughout the different technologies developed
SHINE PV project will demonstrate the integrated innovative processes and novel equipment both virtually, by means of validated simulations setups, and within physical pilots at industrial partners at TRL7. To our knowledge for all these technologies no production equipment is available for HVM worldwide, and we envision a great potential for a PV supply chain revamping in EU sparked by SHINE PV.
WPs structure

Partners' Roles
🔹 Simulation-driven process innovation led by University of Ljubljana, Polymer Competence Center Leoben GmbH (PCCL), and EnginSoft Italy
🔹 Advanced metallization processes developed by Fraunhofer-Institut für Solare Energiesysteme ISE, HighLine Technology GmbH, and CSEM, using nanoparticle pastes from BeDimensional S.p.A., and improvement of the post processing techniques to enhance solar cell efficiency, in cooperation with CEA and Fraunhofer-Institut für Solare Energiesysteme ISE
🔹 New shingling and twill interconnection processes from CEA, Fraunhofer-Institut für Solare Energiesysteme ISE and imec
🔹 Equipment development powered by Applied Materials-IT, CSEM, CEA, Fraunhofer-Institut für Solare Energiesysteme ISE, RENA Technologies GmbH, imec, and IPTE
🔹 Use cases will demonstrate SHINE PV equipment into 3SUN, Qcells Europe and SOLTECH NV production lines. Evaluations for distributed lines will be performed by Kiwa PI Berlin and University of Ljubljana; for the use cases lines by Applied Materials-IT, 3SUN, Qcells Europe and SOLTECH NV; and for digital lines by EnginSoft Italy.
📁 The project is coordinated by Applied Materials-Ireland, with Applied Materials-Italy overseeing technical coordination, and AMIRES Investments s.r.o. managing project execution.